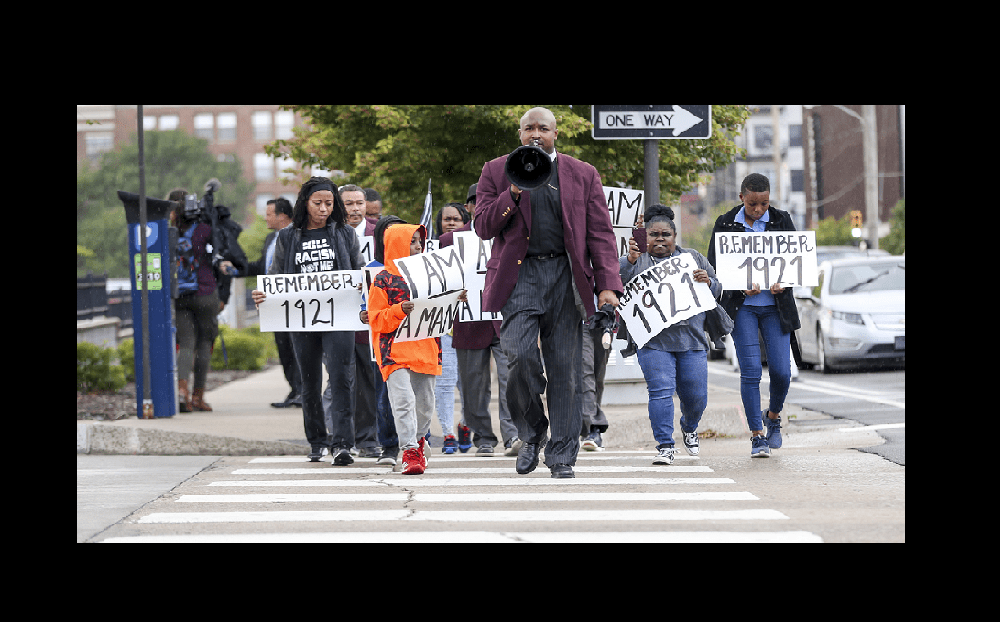Provide Reparations for 1921 ‘Tulsa Race Massacre. State, City Should have a plan to Compensate Survivors
Reverend Robert Turner of the historic Vernon African Methodist Episcopal (AME) church, damaged in the 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre, leads a reconciliatory pilgrimage of sorts from Mount Vernon AME to Tulsa City Hall every Wednesday, demanding “reparations now.” © 2019 Ian Maule/Tulsa World
(Washington, DC) – State and local authorities in Tulsa, Oklahoma should provide reparations for the 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre, when a white mob killed several hundred black people and destroyed a prosperous black neighborhood, Human Rights Watch said in a report released today. They should promptly develop and carry out a comprehensive reparations plan, in close consultation with the local community, to address the harm caused by the massacre and its lasting impact.
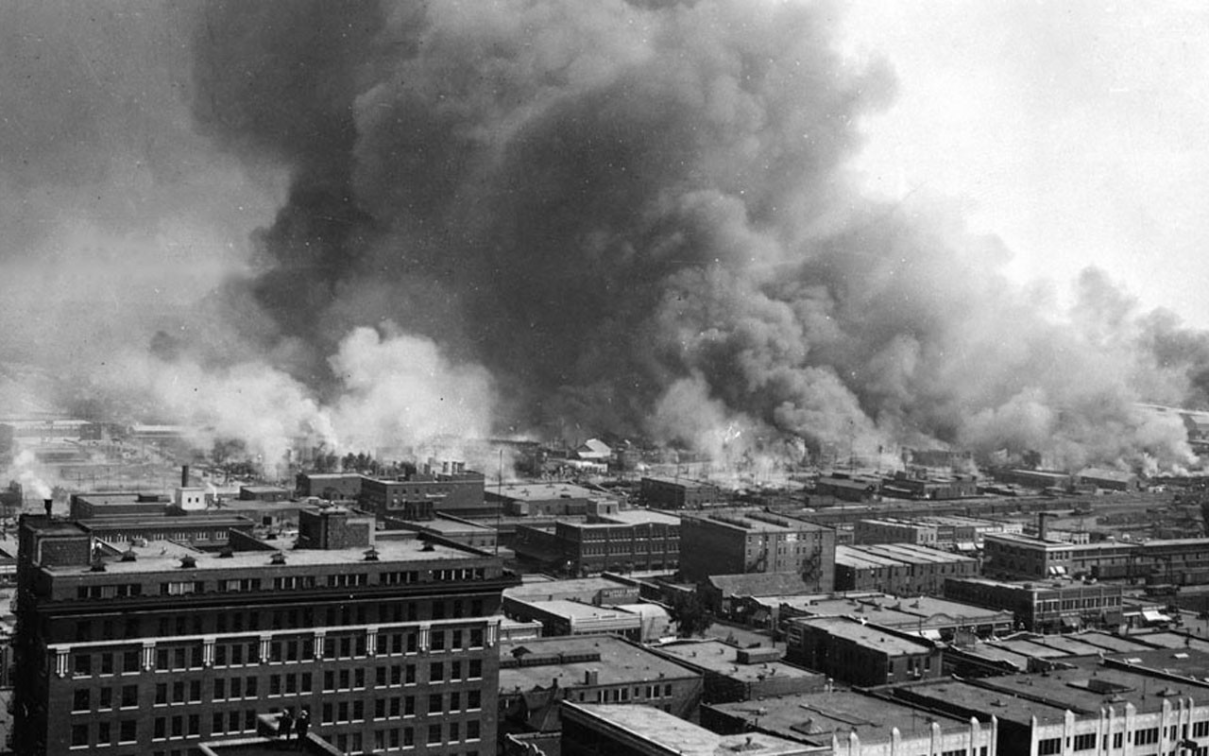
The 66-page report, “The Case for Reparations in Tulsa, Oklahoma: A Human Rights Argument,” details the destruction that left hundreds of people, most of them black, dead and more than 1,200 black-owned houses burned in Tulsa’s Greenwood neighborhood, then known as “Black Wall Street.” Human Rights Watch also described some of the subsequent policies and structural racism that prevented Greenwood and the broader North Tulsa community from thriving. In this context, the US Congress should also pass H.R. 40, a bill that would begin to address the ongoing harm from slavery. Report: The Case for Reparations in Tulsa, OklahomaReport: The Case for Reparations in Tulsa, Oklahoma

Also, Worth Reading
A Perfect Storm Is Brewing in Burundi, Amidst 2020 Election
“It was almost 100 years ago that the Greenwood neighborhood in Tulsa was destroyed, but survivors of the massacre and their descendants are still suffering the consequences,” said Dreisen Heath, US program advocacy officer at Human Rights Watch and author of the report. “Decades of black prosperity and millions of dollars in hard-earned wealth were wiped out in hours but nobody was ever held accountable and no compensation was ever paid.”
The massacre occurred between May 31 and June 1, 1921, after a black man was accused of assaulting a white woman. A white mob, including people deputized and armed by city officials, descended on Greenwood, terrorized black families, and burned their community to the ground. About 35 square blocks – more than 1,200 black-owned houses, scores of businesses, a school, a hospital, a public library, and a dozen black churches – were destroyed and thousands were left homeless. The American Red Cross estimated the death toll at 300, but the exact number remains unknown. Only recently did officials begin limited excavations of unmarked mass graves.
Human Rights Watch, the National African American Reparations Commission, and the American Civil Liberties Union will join leaders from Tulsa and across the US on May 31, 2020 to open a series of virtual forums that will explore the enduring impact of the massacre and the path to reparations in Tulsa and for other African Americans.
In the immediate aftermath, the state declared martial law and the state and local authorities disarmed and arrested black people in Tulsa, moving them to internment camps where thousands of black Tulsans, then homeless, were forced to live in tents. Government officials committed no public money to help Greenwood rebuild. Rather, they impeded rebuilding, even rejecting offers of medical and reconstruction assistance from within and outside Tulsa.
No one was held responsible for the violent crimes, and city and state officials attempted to cover up the massacre for decades. This fall, for the first time, the Oklahoma Education Department will include the race massacre in its curriculum.
In 2003, civil rights lawyers sued Tulsa, its Police Department, and the state of Oklahoma, seeking restitution for the more than 200 survivors and their descendants. A court dismissed the suit, citing the state’s statute of limitations.
Ongoing de facto segregation, discriminatory policies, and structural racism have left black Tulsans, particularly those in North Tulsa, with a lower standard of living and fewer opportunities than other Tulsans. There are significant racial disparities in the city across multiple indicators, from access to health and nutritious food to education. Greenwood community members have expressed concern that the current economic investment plans are not sufficiently focused on supporting the community or preserving its black heritage, but rather on gentrifying the area.
“Tulsa stands out for the malicious destruction during the massacre, but the racist systems, policies, and practices that have harmed black Tulsans over decades are not unique,” Heath said. “In many ways, Tulsa is a microcosm of the United States.”
The massacre occurred in a broader context of systemic racism rooted in the US history of slavery, white supremacy, racist violence, and oppression, which continues across the United States today, Human Rights Watch said.
Under international human rights law, governments have an obligation to provide effective remedies for human rights violations like the Tulsa massacre, including through a range of reparations mechanisms.
Human Rights Watch has long supported the development of broader reparations plans to account for the cruelty of slavery and subsequent harm, and supports US House Resolution 40, to establish a commission to examine the impact of the slave trade and to recommend ways to address the harm, including apology and compensation. This bill has gained traction, with nearly 100 new co-sponsors, an indication of growing recognition of the importance of accounting for the impact of slavery and decades of racist, discriminatory laws and practices that followed and persist today.
The Tulsa and Oklahoma governments should act swiftly to provide reparations, including direct payments to the few massacre victims still living and their descendants, and to recover and identify remains that may be in mass graves. The state and local governments should promptly establish a comprehensive reparations plan such as by strengthening existing scholarship programs, funding memorials, and providing targeted investments in health, education, and economic opportunities, in close consultation with affected community members. Federal, state, and local authorities should also pass legislation to clear legal barriers to civil legal claims related to the massacre.
“Tulsa officials failed to deliver on promises to provide full reparation, harming black life in Tulsa from the massacre to the present day,” Heath said. “Government authorities have an opportunity to fully reckon with these historical and contemporary wrongs by finally doing what they should have done a long time ago – providing reparations to massacre descendants and the black people in Tulsa today.”
For more on the Virtual Forums on the Tulsa Race Massacre and Reparations, please visit:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PgusoVPh5K0&feature=youtu.be
To support a petition calling on the Tulsa and Oklahoma governments to make full reparations to survivors and descendants of the Tulsa Race Massacre, please visit: https://www.change.org/tulsareparationsnow
Human Rights Watch Image source Wikipedia