Diesel fuel has long been a crucial component in the transportation industry. Known for its efficiency and energy density, diesel has powered a significant portion of the world’s vehicles and machinery, from trucks and buses to agricultural and construction equipment. In a world rushing toward gas alternatives, it’s worth learning the most interesting facts about diesel fuel and how it impacts you and the transportation industry.
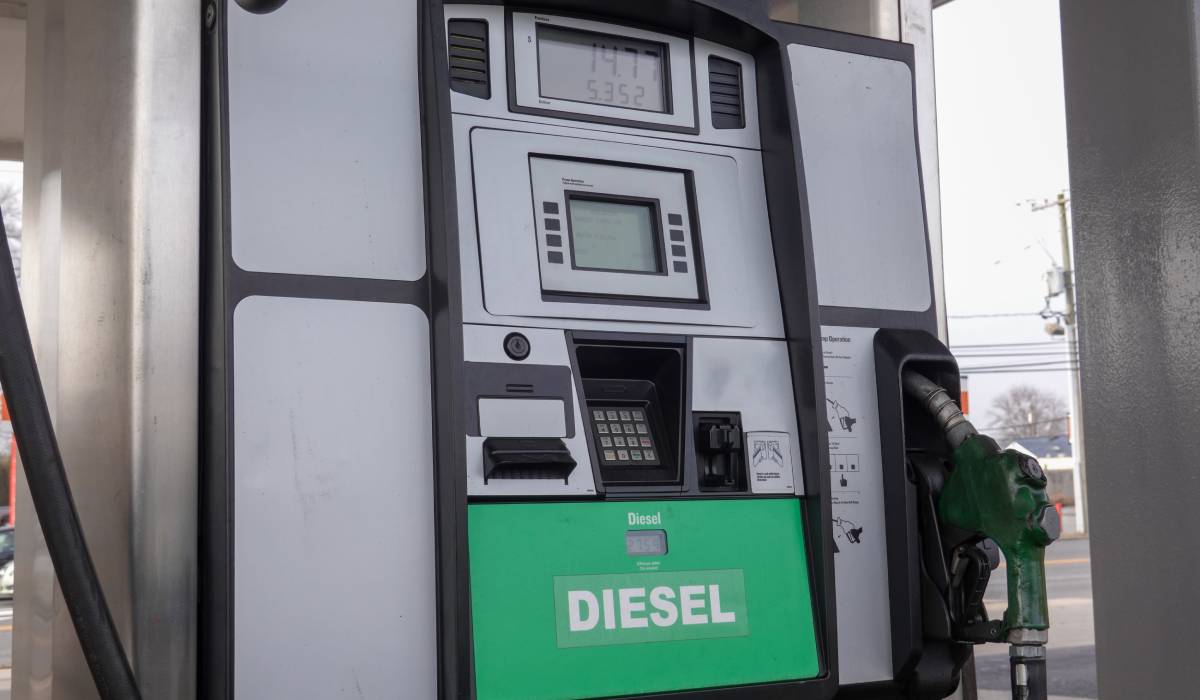
What Is Diesel?
Diesel is a type of fuel derived from crude oil and is used primarily in compression ignition engines, which are typically found in larger vehicles and machinery. Named after Rudolf Diesel, who invented the diesel engine in the late 19th century, this fuel is known for its higher energy efficiency compared to gasoline. It has a higher boiling point and energy density, allowing vehicles to travel further on less fuel. Diesel is composed of hydrocarbons and is often blended with biofuels to reduce emissions and promote sustainability. Unlike gasoline engines that use spark plugs, diesel engines compress air until it heats up and then injects fuel into the hot air, causing it to ignite spontaneously. This process results in robust performance and durability.
Superior Fuel Efficiency
One of the most compelling advantages of diesel fuel is its superior fuel efficiency compared to gasoline. Diesel engines are generally 20–30 percent more efficient, meaning vehicles require less fuel to cover the same distance. This efficiency arises from the diesel engine’s higher compression ratio, which allows it to extract more energy from each unit of fuel. As a result, vehicles powered by diesel can achieve remarkable miles per gallon, proving particularly essential for industries like freight and logistics, where fuel costs are a critical concern.
Trucks Run on Diesel
Diesel fuel has long retained a profound impact on the trucking industry, serving as its backbone for decades. With its superior energy efficiency and power, diesel allows trucks to travel long distances carrying heavy loads, making it the preferred choice for long-haul transportation. The energy density of diesel means that trucks can achieve better fuel economy, reducing operational costs for trucking companies. Additionally, the durability and reliability of diesel engines contribute to fewer breakdowns and maintenance issues, ensuring that supply chains remain uninterrupted.
Diesel Fuel in the Winter
When temperatures drop during the winter months, special precautions must be taken with diesel fuel to ensure it remains effective and accessible. Diesel fuel can gel in extremely cold temperatures due to the waxy components in the fuel solidifying, which can clog fuel lines and filters, leading to engine performance issues. To prevent this, a winterized diesel blend, often containing additives like anti-gel agents, is recommended to lower the pour point and improve cold flow properties. In addition, fuel suppliers should protect their diesel fuel pumps with reliable insulation blankets and related cold-weather solutions.
Whether it’s serving as the fuel of choice for trucks or offering superior energy efficiency, diesel continues to play a significant role in the transportation industry. By learning more about the interesting facts about diesel fuel, you can gain a greater understanding of traditional gas alternatives and make a more positive impact on the environment.